Current That Continually Reverses Direction is Known as
Alternating Current
In electricity, alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction, flowing in one direction for a period of time and then reversing direction and flowing in the other direction for a period of time. This is in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows continuously in one direction. If the direction of the current continually reverses, it is called alternating current. If it reverses back and forth (alternately reversing directions), it is called cyclic alternating current or AC. In the United States, the current that most commonly varies direction is the 220-volt conventional (household) AC, while the current used for power is in the 110-volt range. However, the latter current is also commonly referred to as AC, as it is also a form of AC. In other countries, the systems are reversed.

Physics
An RLC series circuit is connected to a $240-\mathrm{V}$ ms power supply at a frequency of $2.50 \mathrm{kHz}$. The elements in the circuit have the following values: $R=12.0 \Omega, C=$ $0.26 \mu \mathrm{F},$ and $L=15.2 \mathrm{mH},$ (a) What is the impedance of the circuit? (b) What is the rms current? (c) What is the phase angle? (d) Does the current lead or lag the voltage? (e) What are the rms voltages across each circuit element?


Essential University Physics
A $470-\Omega$ resistor, 10 - $\mu \mathrm{F}$ capacitor, and 750 -mH inductor are each connected across $6.3-\mathrm{V}$ rms, $60-\mathrm{Hz}$ AC power. Find the rms current in each.

Essential University Physics
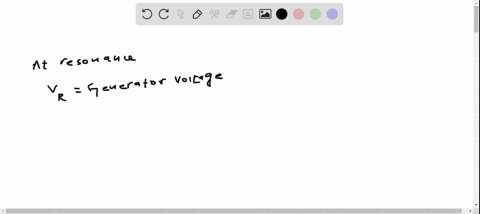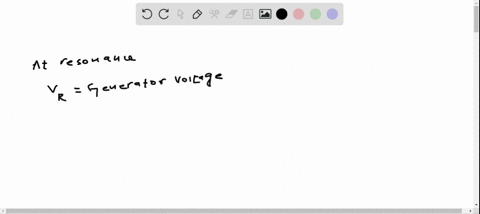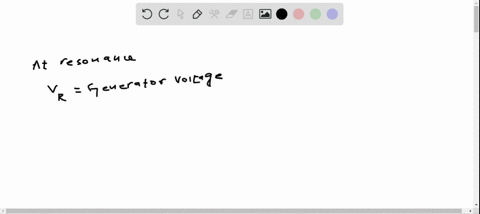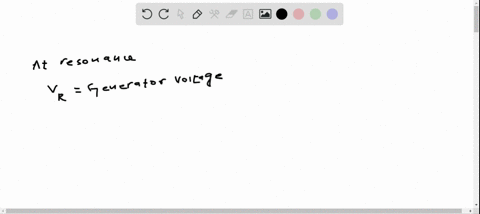
If you measure the rms voltages across the resistor, capacitor, and inductor in a series $R L C$ circuit, will they add to the rms generator voltage?

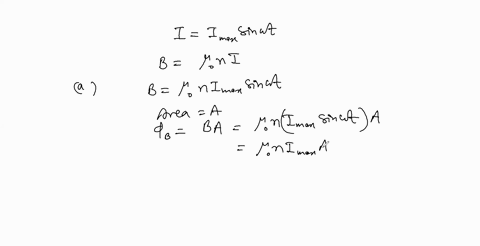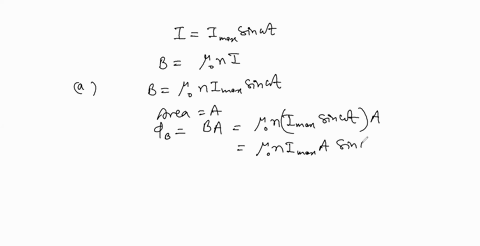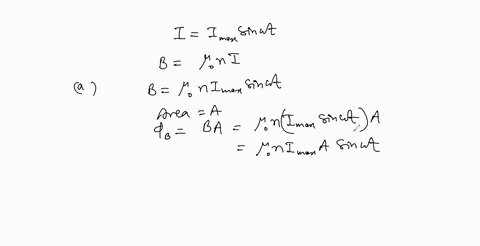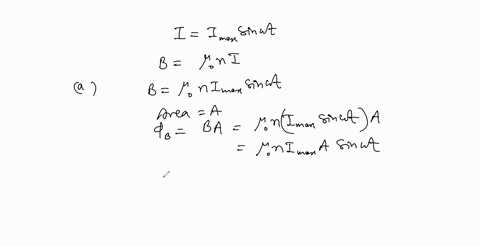
Principles of Physics a Calculus Based Text
When a wire carries an AC current with a known frequency, you can use a Rogowski coil to determine the amplitude $I_{\max }$ of the current without disconnecting the wire to shunt the current through a meter. The Rogowski coil, shown in Figure $P 23.8,$ simply clips around the wire. It consists of a toroidal conductor wrapped around a circular return cord. Let $n$ represent the number of turns in the toroid per unit distance along it. Let $A$ represent the cross-sectional area of the toroid. Let $I(t)=$ $I_{\max } \sin \omega t$ represent the current to be measured. (a) Show that the amplitude of the emf induced in the Rogowski coil is $\varepsilon_{\max }=\mu_{0} n A \omega I_{\max } .$ (b) Explain why the wire carrying the unknown current need not be at the center of the Rogowski coil and why the coil will not respond to nearby currents that it does not enclose.

University Physics
Can the instantaneous power output of an ac source ever be negative? Can the average power output be negative?

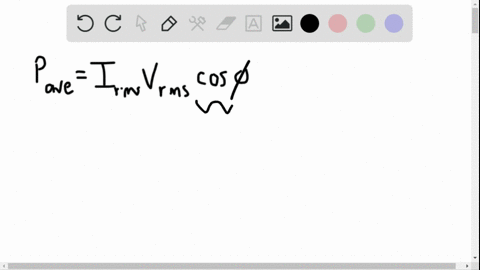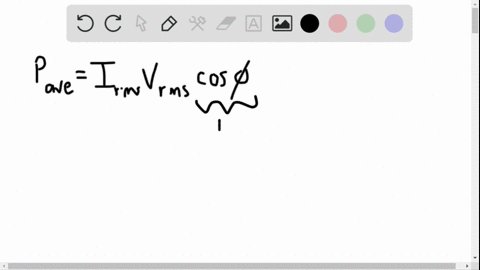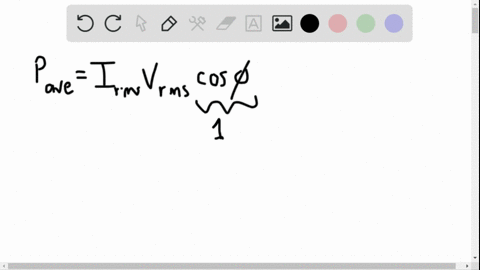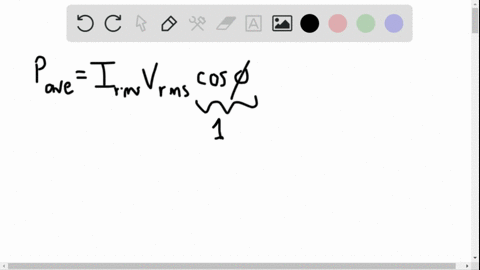
University Physics
For what value of the phase angle $\phi$ between the voltage output of an ac source and the current is the average power output of the source a maximum?

University Physics
Semi-tractor trucks use four large $12-\mathrm{V}$ batteries. The starter system requires 24 V, while normal operation of the truck's other electrical components utilizes 12 V. How could the four batteries be connected to produce 24 V? To produce 12 V? Why is 24 V better than 12 V for starting the truck's engine (a very heavy load)?

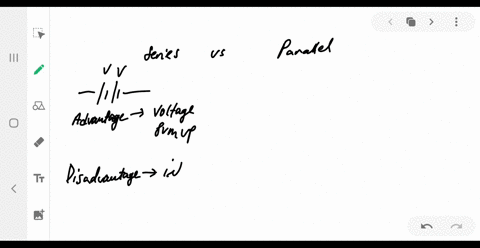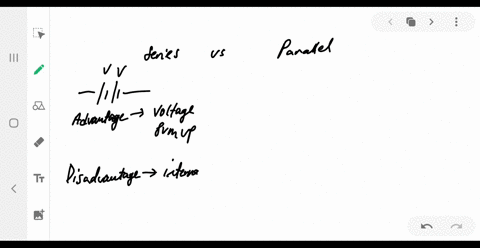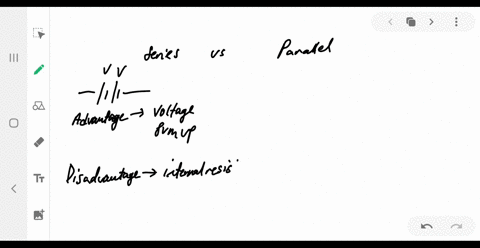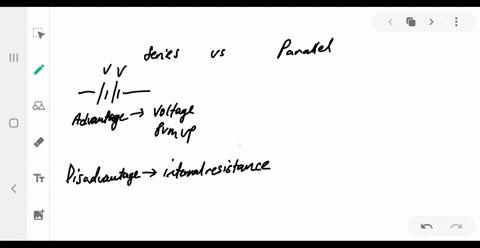
University Physics
What are the advantages and disadvantages of connecting batteries in series? In parallel?

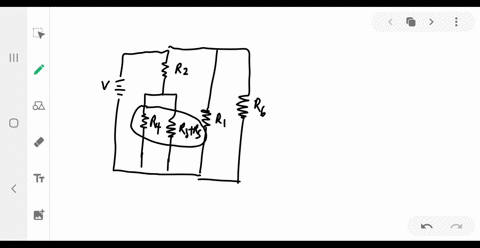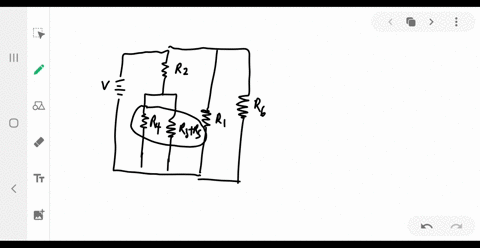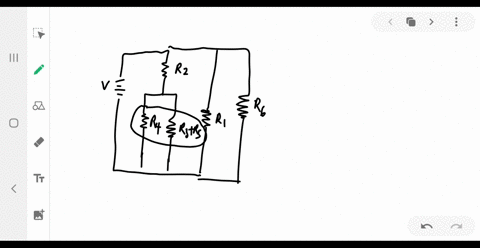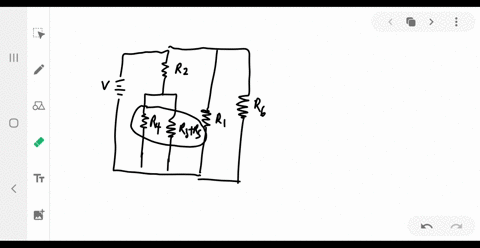
University Physics
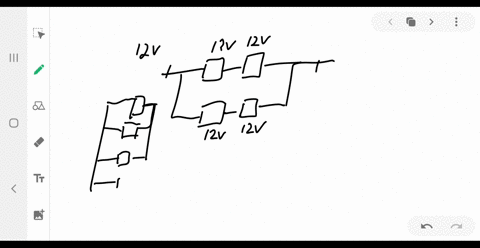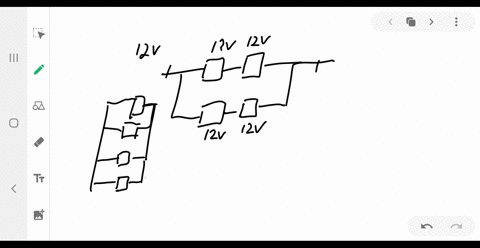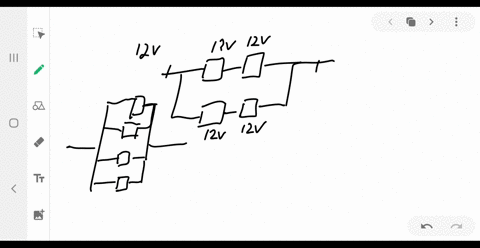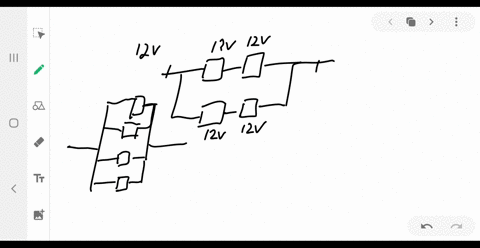
Consider the circuit shown below. Does the analysis of the circuit require Kirchhoff's method, or can it be redrawn to simplify the circuit? If it is a circuit of series and parallel connections, what is the equivalent resistance?


University Physics
Why do transmission lines operate at very high voltages while household circuits operate at fairly small voltages?

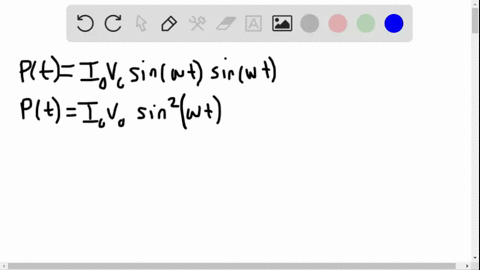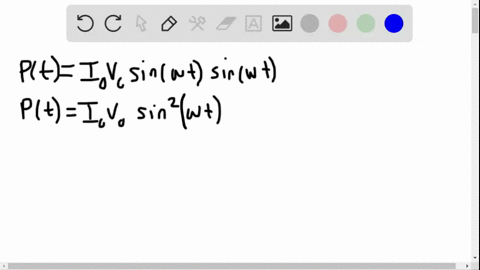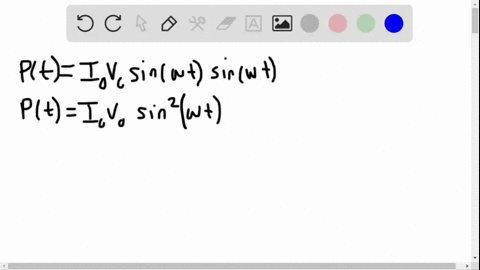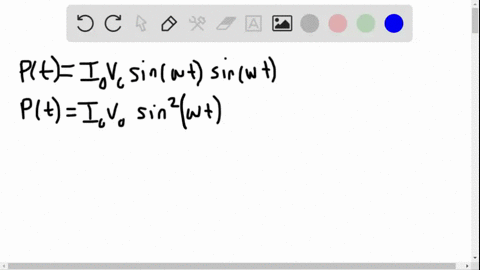
University Physics
The power rating of a resistor used in ac circuits refers to the maximum average power dissipated in the resistor. How does this compare with the maximum instantaneous power dissipated in the resistor?

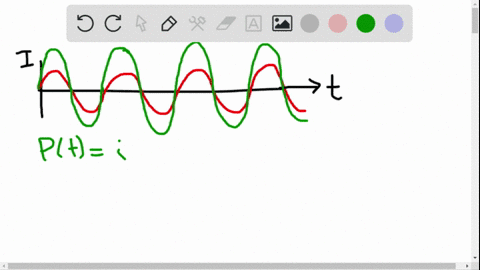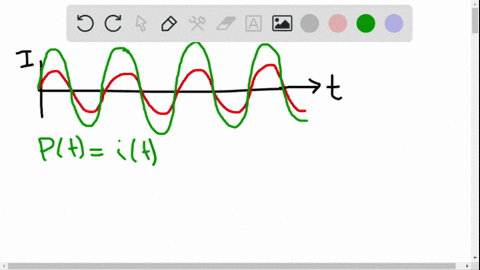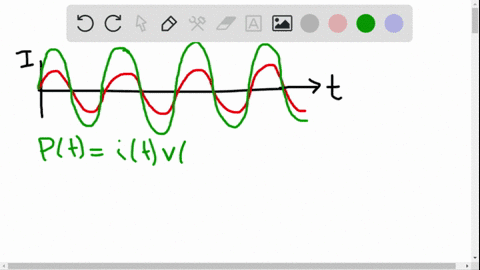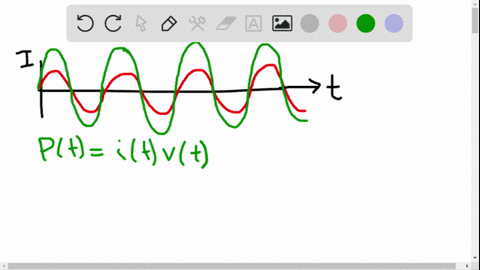
University Physics
The average ac current delivered to a circuit is zero. Despite this, power is dissipated in the circuit. Explain.

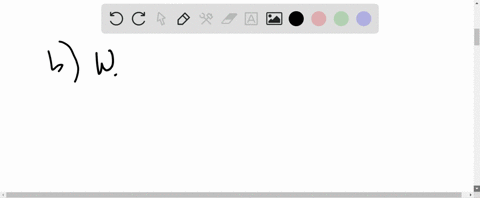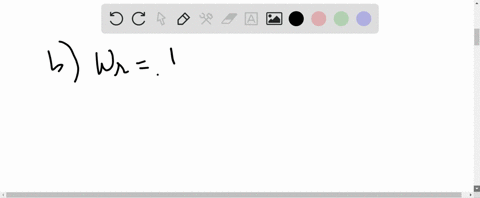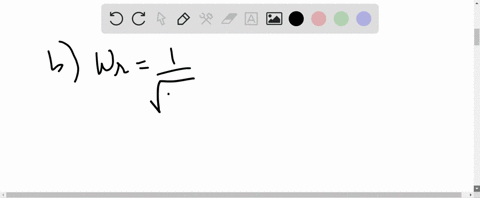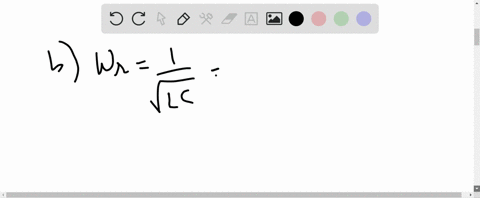
University Physics with Modern Physics
A series circuit consists of an ac source of variable frequency, a $115-\Omega$ resistor, a $1.25-\mu F$ capacitor, and a $4.50-\mathrm{mH}$ inductor. Find the impedance of this circuit when the angular frequency of the ac source is adjusted to (a) the resonance angular frequency; (b) twice the resonance angular frequency; (c) half the resonance angular frequency.

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
In a certain $L R C$ series circuit, when the ac voltage source has a particular frequency $f$ , the peak voltage across the inductor is 6.0 times greater than the peak voltage across the capacitor. Determine $f$ in terms of the resonant frequency $f _ { 0 }$ of this circuit.


Physics: Principles with Applications
A flashlight can be made that is powered by the induced current from a magnet moving through a coil of wire. The coil and magnet are inside a plastic tube that can be shaken causing the magnet to move back and forth through the coil. Assume the magnet has a maximum field strength of 0.05 T. Make reasonable assumptions and specify the size of the coil and the number of turns necessary to light a standard 1-watt, 3-V flashlight bulb.

University Physics
Will a transformer work if the input is a dc voltage?


University Physics
How can you distinguish the primary winding from the secondary winding in a step-up transformer?


Essential University Physics
A step-up transformer increases voltage, or energy per unit charge. Why doesn't this violate energy conservation?

connollymarmuccuself.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.numerade.com/topics/alternating-current/
0 Response to "Current That Continually Reverses Direction is Known as"
Post a Comment